By default VUM ( VMware vSphere Update Manager ) supports only one VC instance and it can’t support multiple VCs simultaneously but having the VUM utility we can re-configure the second VC separately to use the same update manager .
This method is not supported by VMware and in case of serious SQL licensing issue or other cost factor, we can try this method to use the single VUM for multiple VC instances and in my lab I have configured two VCSA ( Vcenter Appliance ) and updating the host using the single same VUM.
Intial stage of the VUM installation itself we have to configure the vCenter instance and based on the size of the inventory we have to chose the Database , The Update Manager server and Update Manager Download Service require a database to store and organize server data. Its recommended to have the separate VUM database from the VC and VC database. Before installing the Update Manager server, you must create a database instance and configure it to ensure that all Update Manager database tables can be created in it. If you are using Microsoft SQL Server 2008 R2 Express, you can install and configure the database when you install Update Manager. Microsoft SQL Server 2008 R2 Express is used for small deployments of up to 5 hosts and 50 virtual machines.
Although you can install the Update Manager server only on 64-bit machines, Update Manager is a 32-bit application and requires a 32-bit DSN.

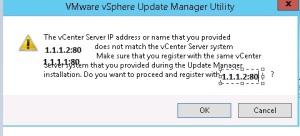
VUM has a utility called VMwareUpdateManagerUtility.exe in which we can re-register the vCenter Server . For EX we can install the VUM plugin to the first VCSA 1.1.1.1 and update the ESX host. Later we can re-configure the VUM by running the utility and it will ask for the option to give the VC name or IP in which we can provide the second VC IP address .
Once we provided the VC IP it will show the warning and we have to accept and reboot the VUM service on VUM server.
By login to the VC we can find the VUM plugin on the second VC , Since VUM uses the same DB we can find the same baseline which was configured on first VC or else we can create the new baseline for the newly connected VC.
At the same time on the first VC , it will show the below error on connecting the VUM plug-in and if we want to update the host running on first VC again re-configure the same steps with the VC IP or Name.
Reference : https://pubs.vmware.com/vsphere-51/index.jsp#com.vmware.update_manager.doc/GUID-B5FB88E4-5341-45D4-ADC3-173922247466.html








Nice post – but to work like that on a daily basis is just shmooo – why don’t VMware give us a Update Manager Server supporting several vCenter Servers?
LikeLike
Any good reason it cannot be pointed to a hostname and then the hostname mapped to a different IP address through the local hosts file on the VUM server, making it point to whatever vCenter without a need to re-register?
I can see it may require certs to be accepted/installed/validated for vCenter, which is not meant to be an issue ever since the vsphere 6 has those signed by PSC.
LikeLike
worked for me, I used to it to move off a vcenter 2012 server to a vcenter appliance and redirect the update manager to the new vc appliance. Not sure why a the update manager can handle more than one vcenter.
LikeLike